Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Abstract
The proliferation of Speech-to-Text (STT) models and APIs necessitates objective performance benchmarks that reflect real-world conditions. Existing evaluations often fall short, either focusing on theoretical model capabilities or exhibiting bias from self-interested providers. This paper presents a practical and neutral benchmark of seven leading STT models, including open-source options like Whisper and Distil-Whisper, and proprietary APIs such as IBM Granite-speech-3.3, Deepgram, and AssemblyAI. Our methodology emphasizes real-world transcription challenges, particularly in high-stakes environments, utilizing a diverse dataset with clean and noisy speech. We evaluate models based on Word Error Rate (WER) and its components (substitutions, deletions, insertions), as well as Character Error Rate (CER). Findings indicate that Granite-Speech-3.3 consistently outperforms other models across both clean and noisy conditions, demonstrating superior accuracy and robustness. Distil-Whisper shows strong performance, particularly in CER, making it a viable option for resource-constrained applications. Wav2Vec2, however, exhibits significant limitations, rendering it unsuitable for production-grade use. This benchmark provides crucial insights for developers and product teams seeking reliable STT solutions for real-world scenarios where accuracy is paramount.
1 Introduction
The landscape of Speech-to-Text (STT) models and APIs is rapidly expanding, leading to a critical need for unbiased and reliable performance evaluations. Developers and product teams often struggle to answer the fundamental question: “Which STT solution should I use?” This challenge is exacerbated by the limitations of current benchmarking practices.
Academic research, while valuable for understanding model architectures, typically focuses on isolated model comparisons rather than their performance within production-grade APIs. These studies often overlook real-world constraints such as latency, computational cost, and diverse acoustic conditions. Conversely, many online API benchmarks are conducted by the providers themselves, leading to inherent biases where their own solutions are consistently ranked at the top. A prominent example is Deepgram’s benchmark, which, unsurprisingly, positions Deepgram first across all metrics. While strategically sound from a marketing perspective, such evaluations offer limited utility for developers seeking objective and reliable comparisons based on realistic scenarios.
This benchmark was initiated out of a practical necessity for a more neutral and robust evaluation. Our primary objective was not to generate clickbait or marketing collateral, but to answer a crucial question: “Which speech-to-text model can actually be trusted when accuracy isn’t optional?” We specifically focused on real-world transcription challenges, particularly those encountered in high-stakes environments like hospitals, where even a single transcription error can lead to serious consequences. This benchmark is meticulously designed to assist developers and product teams in selecting the most appropriate STT model for real-world speech processing, moving beyond idealized lab conditions to assess actual performance under duress.
2 Methodology
Our evaluation focused on real-world conditions that present significant challenges for speech recognition systems.
2.1 Dataset Description and Real-World Relevance
Dataset Overview:
- Total audio clips: 58
- Duration: 5 to 40 seconds per clip
- Categories:
- Clean Speech: Recorded in quiet, echo-free environments.
- Noisy Speech: Includes real-world ambient noise such as crowd chatter, movement, room reverb, or mild background static.
- Speakers: Human-recorded audio clips sourced from workers using Ionio, covering diverse accents and speaking styles.
- Format: WAV, 16 kHz, mono-channel (standard for most ASR systems).
Audio Specifications:
- Format: WAV
- Processing: Standardized to 16 kHz sample rate for model compatibility.
- Variety: Diverse accent patterns and environmental conditions.
- Challenge level: High, combining accent variation with noise interference.
The dataset is publicly available for review and use at:
https://huggingface.co/datasets/Ionio-ai/speech_to_text_benchmark/tree/main
2.2 Evaluated Models
We tested seven leading speech-to-text models representing different approaches to automatic speech recognition:
- Whisper (OpenAI): High accuracy in clean speech, strong multilingual support, available in multiple sizes.
- Deepgram: Excels in real-time transcription and noisy environments, with low latency.
- AssemblyAI: High accuracy in clean and noisy speech, strong formatting capabilities.
- Wav2Vec2: Offers versatility for custom ASR systems, integrating seamlessly with Hugging Face.
- Distil-Whisper: Is 6x faster and 49% smaller, performing within 1% WER of Whisper, ideal for resource-constrained applications.
- NVIDIA Parakeet 0.6B v2: Nvidia’s fast and efficient, research-grade model with 0.6B parameters.
- IBM Granite-speech-3.3: High-accuracy closed-weight model with state-of-the-art deletion and WER performance with 8B parameters.
2.3 Evaluation Metrics
Word Error Rate (WER) was our primary evaluation metric, widely used to quantify transcription accuracy. We also analyzed the specific types of errors that contribute to WER: substitutions, deletions, and insertions. These individual components often have outsized effects in real-world use cases.
Where:
- S = Number of substitutions (incorrect words)
- D = Number of deletions (missing words)
- I = Number of insertions (extra words)
- N = Total number of words in ground truth
Lower WER indicates better transcription quality, with 0% WER representing perfect accuracy.
2.3.1 Significance of Error Types in Domain-Specific Applications
While WER provides a summary view, understanding how a model makes mistakes is equally important, particularly in domains like healthcare, law, or live broadcasts where each word may carry critical meaning:
- Substitution (S): Replacing “dose” with “those” in a medical instruction could cause dangerous confusion.
- Deletion (D): Omitting “not” in “Do not resuscitate” flips the intent entirely.
- Insertion (I): Adding “no” in “The test was positive” introduces ambiguity or contradiction.
We also tracked Character Error Rate (CER) to capture more granular errors in spellings or names, important for applications like transcribing names, emails, or short codes.
2.4 Inference Strategy: Multi-Pass vs. Zero-Pass Inference
To better understand model stability and variability, we evaluated open-source models under two inference setups:
- Multi-Pass: For models like Whisper, Distil-Whisper, Wav2Vec2, and Parakeet, we averaged results over three inference passes using a temperature of 0.3.
- Zero-Pass: All models, including proprietary APIs, were evaluated once with deterministic decoding (no randomness) for a direct head-to-head comparison.
2.5 Noise Augmentation Strategy
Our augmentation pipeline was designed to simulate diverse acoustic distortions:
- Gaussian Noise: Added to every sample in the noisy set.
- Time Stretching (50% probability): Speed altered between 0.8× (slower) and 1.25× (faster).
- Pitch Shifting (50% probability): Altered pitch by ±4 semitones.
3 Benchmark Analysis Results for Open-Sourced Models
3.1 Clean Speech Evaluation
For clean audio conditions, Granite-Speech-3.3 emerged as the standout performer with an exceptional 8.18% WER, significantly outpacing all competitors. Distil-Whisper secured second place with a respectable 14.93% WER, offering a good balance of accuracy and efficiency. Wav2Vec2 struggled considerably in this category, posting a disappointing 37.04% WER.
3.2 Noisy Speech Evaluation
The introduction of background noise revealed interesting shifts in model robustness. Granite-Speech-3.3 maintained its leading position with 15.72% WER, demonstrating exceptional noise resilience. Distil-Whisper showed strong noise handling capabilities, achieving 21.26% WER, while standard Whisper experienced more significant degradation, jumping to 29.80% WER. Wav2Vec2 remained the weakest performer at 54.69% WER. ) 
3.3 Error Pattern Analysis
3.3.1 Insertion Errors
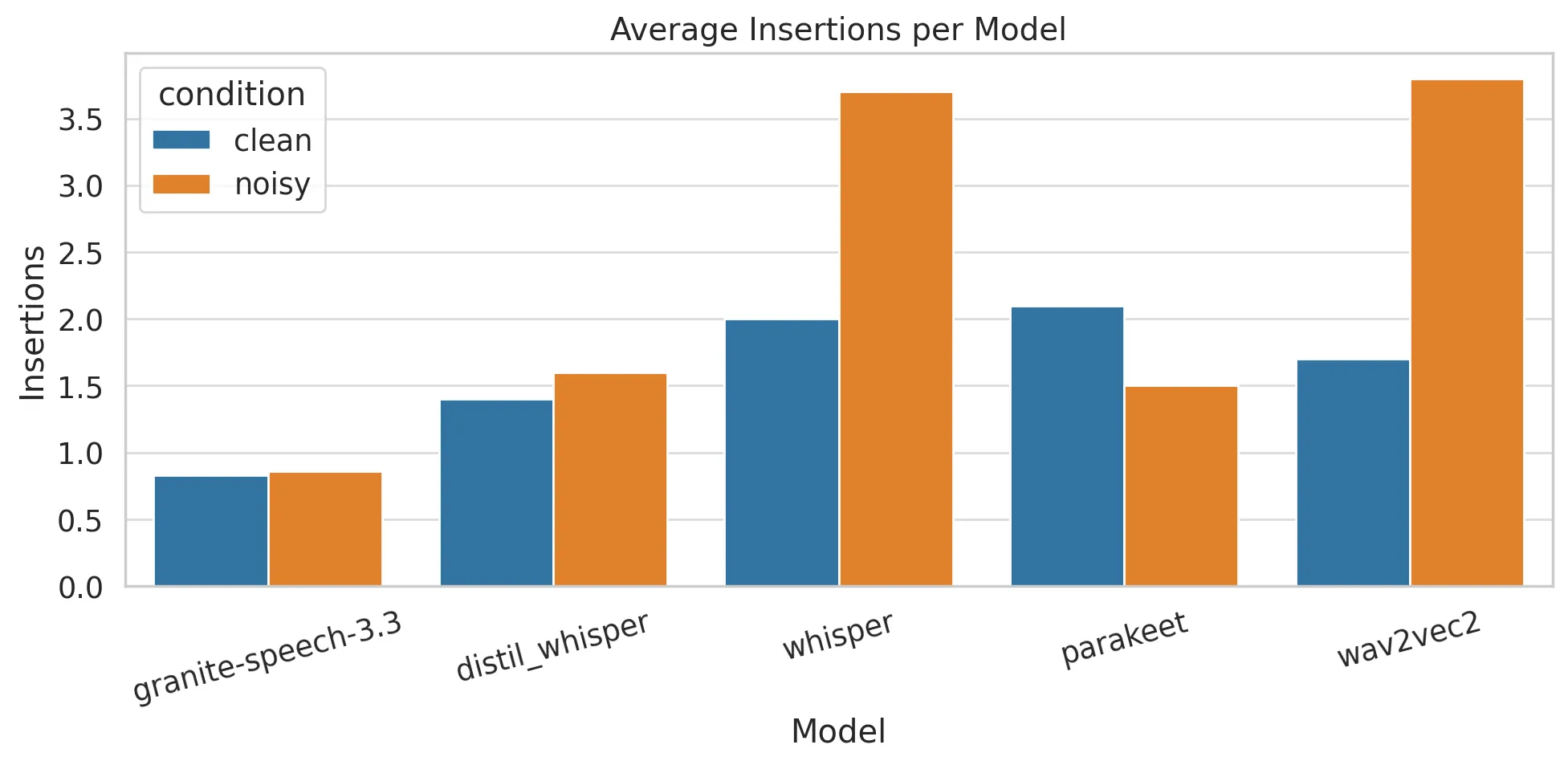
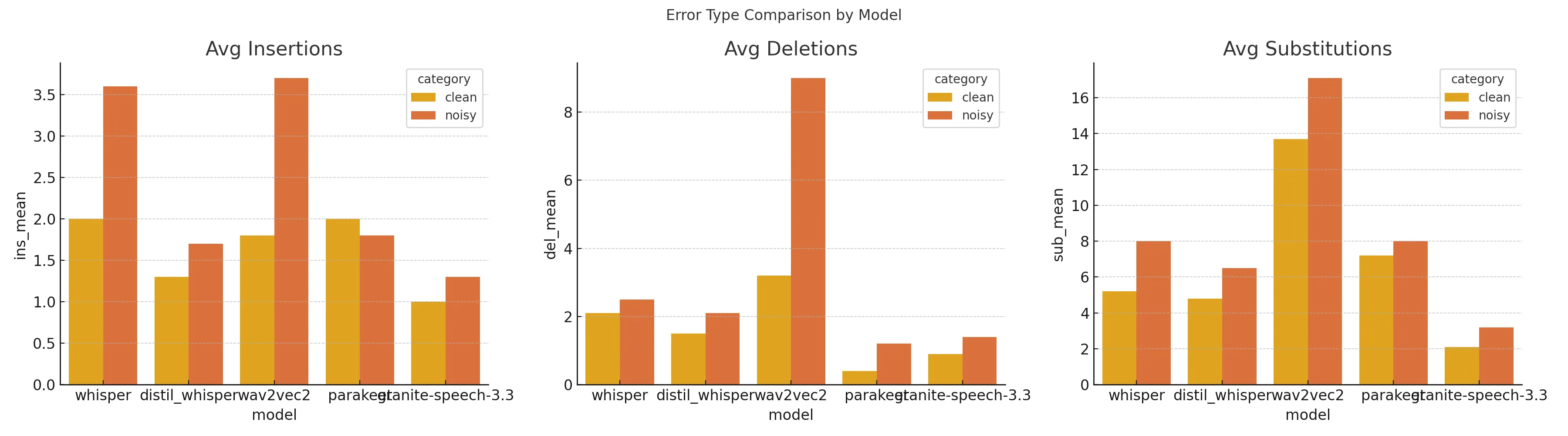
Granite-Speech-3.3 demonstrated minimal insertion errors (0.828 clean, 0.862 noisy), making it suitable for real-time systems that demand accuracy. Whisper, however, showed a sharp increase in insertion errors under noisy conditions, reaching 2.362.
3.3.2 Deletion Errors
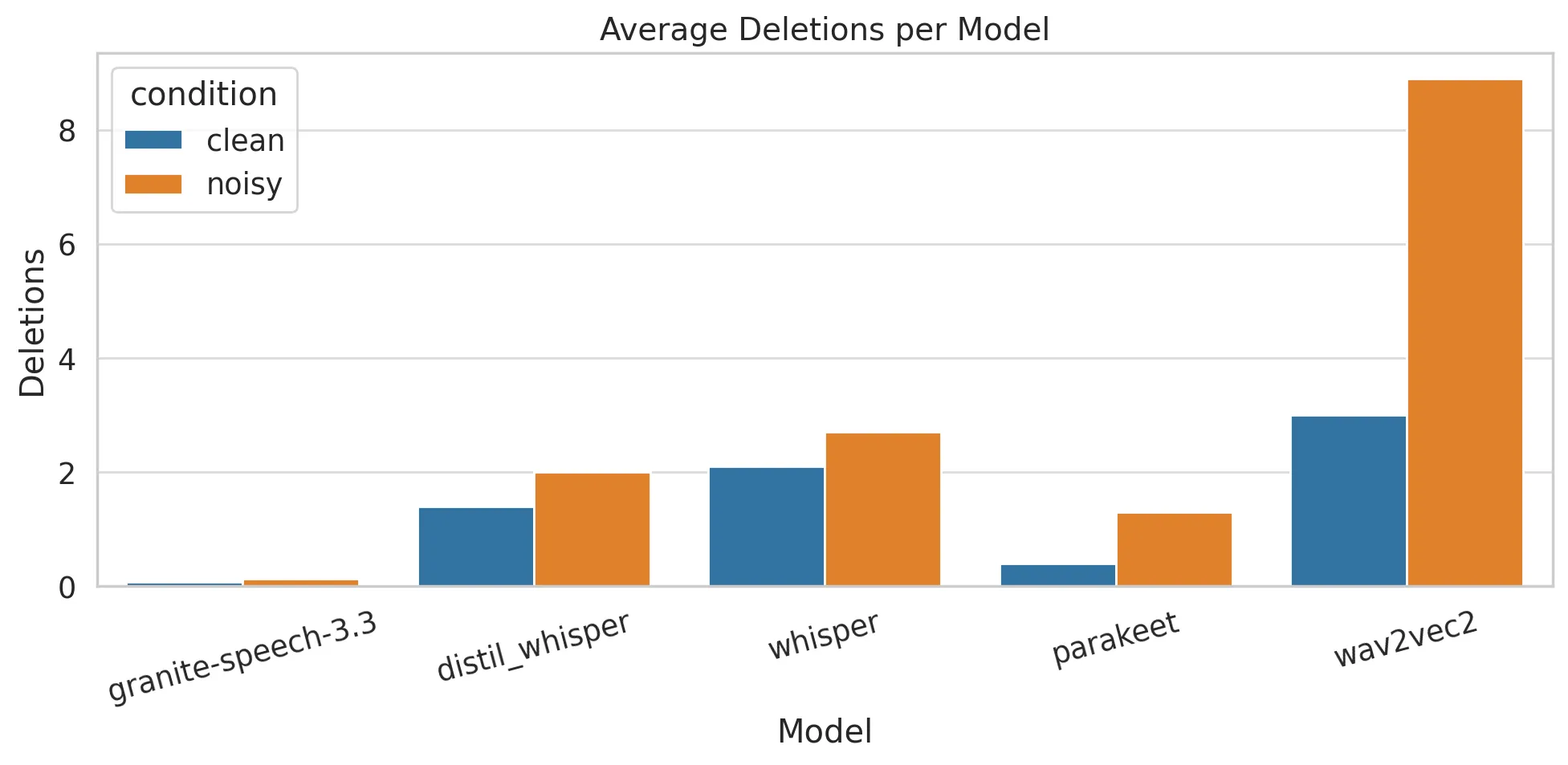
Parakeet led the field in this category with a deletion error rate of just 0.414 under clean conditions, making it well-suited for controlled environments where completeness is non-negotiable. Wav2Vec2 had a deletion rate of 8.897 under noise, suggesting a frequent tendency to drop entire phrases.
3.3.3 Substitution Errors
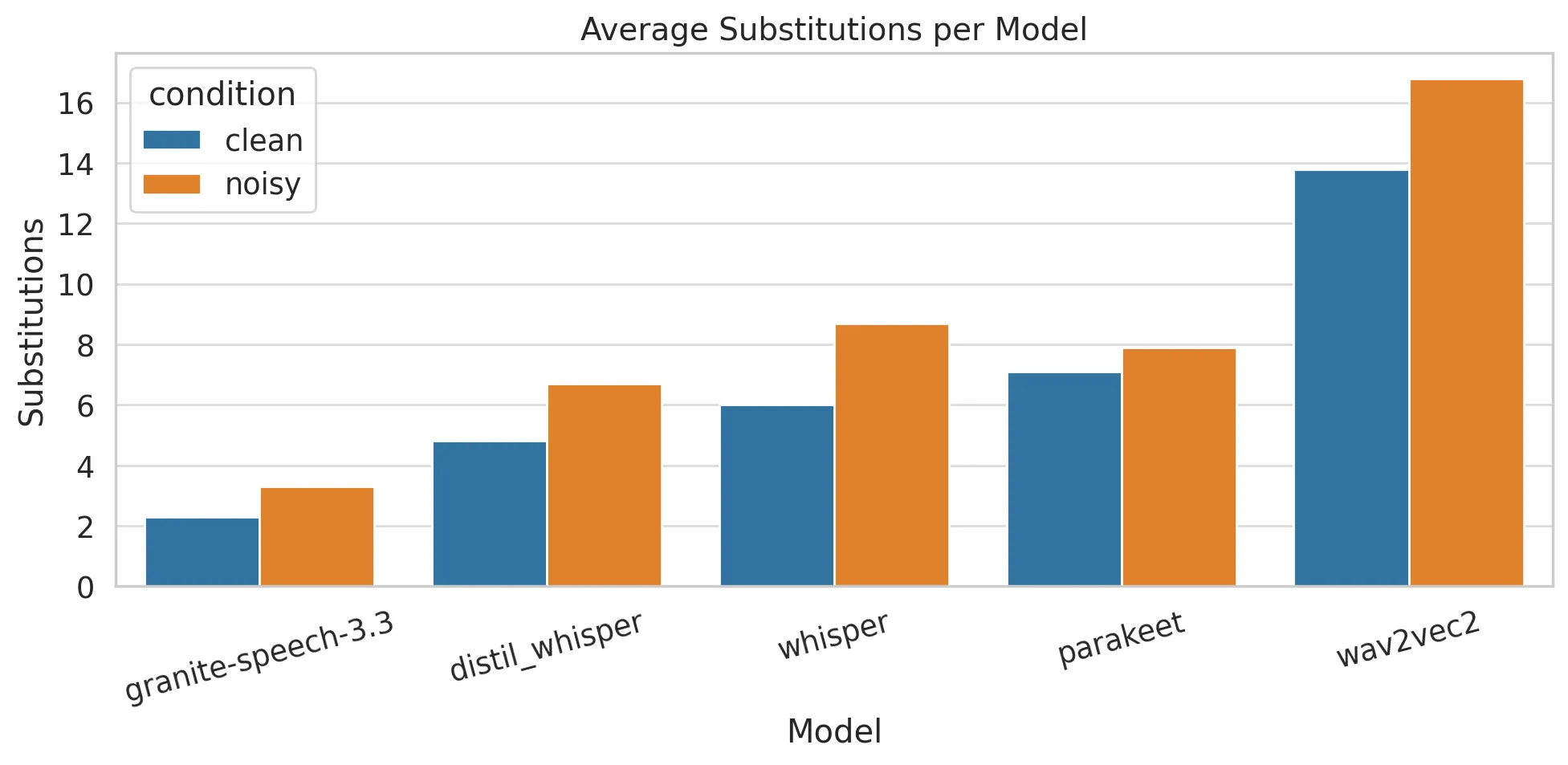
Granite-Speech-3.3 again led with the lowest substitution rates, scoring 2.276 in clean and 3.276 in noisy conditions. Distil-Whisper delivered moderate substitution rates. Wav2Vec2’s substitution error rate ballooned to 13.879 under noisy conditions.
3.4 Character vs Word Error Analysis
The correlation between WER and CER showed a strong alignment across models. Granite-Speech-3.3 achieved the best CER performance (10.26% overall), while Distil-Whisper led in pure CER metrics (10.14%), demonstrating excellent character-level precision.
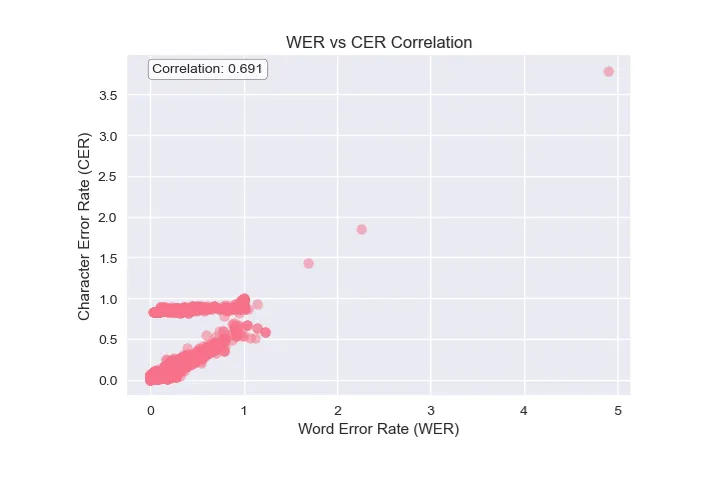
4 Benchmark Analysis Results for All Models
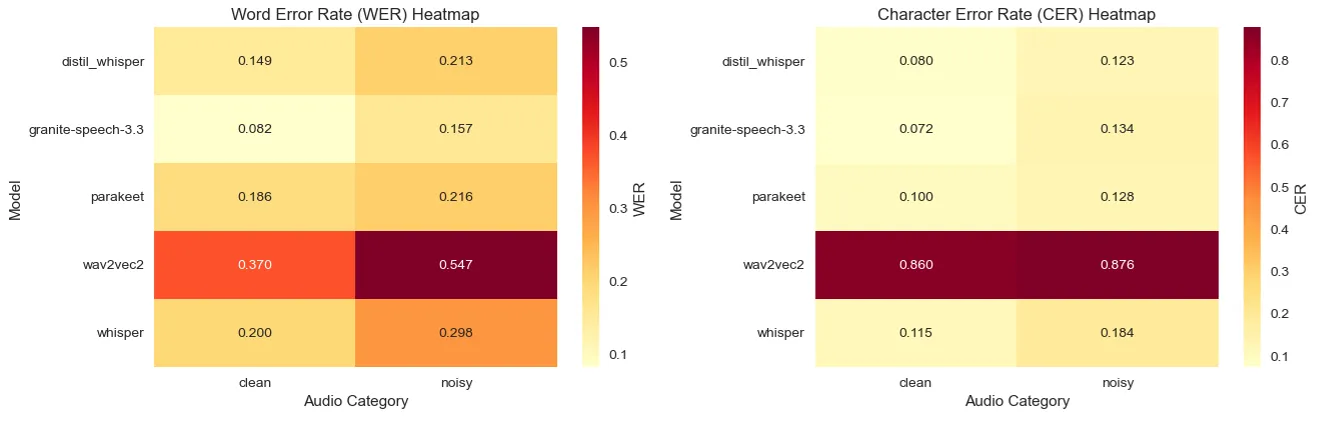
4.1 Clean Speech Evaluation (All Models)
In clean audio conditions, Granite-Speech-3.3’s exceptional 7.9% WER positions it as the leader. AssemblyAI and Parakeet, with WERs of 9.4% and 9.5%, perform admirably. Wav2Vec2’s 29.0% WER indicates significant struggles.
4.2 Noisy Speech Evaluation (All Models)
Granite-Speech-3.3 maintains its dominance with an 11.5% WER in noisy conditions, experiencing only a modest 3.5% increase from clean audio. AssemblyAI’s 14.1% WER also demonstrates notable robustness. Wav2Vec2’s drastic jump to 49.6% WER reveals a critical weakness.
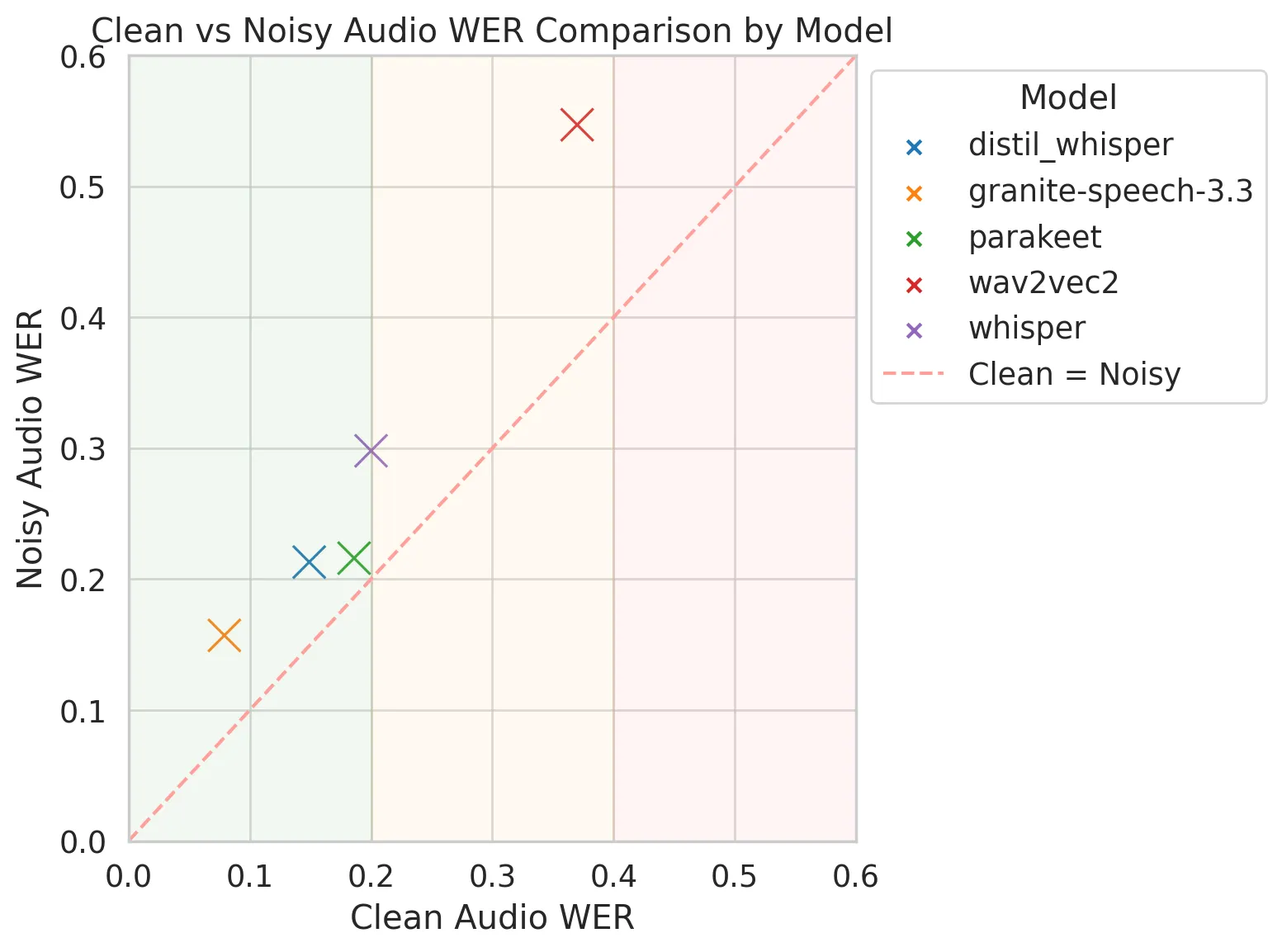
4.3 Error Pattern Analysis (All Models)
- Insertion Errors: Granite-Speech-3.3’s minimal insertion rates (0.828 in clean, 0.862 in noisy) make it ideal for real-time systems.
- Deletion Errors: Parakeet’s low deletion rate of 0.414 in clean conditions makes it a top choice for controlled settings.
- Substitution Errors: Granite-Speech-3.3’s low rates (2.276 clean, 3.276 noisy) are ideal for applications where precision in terminology is paramount.
- Performance in Noisy Conditions: Granite-Speech-3.3’s modest 3.5% WER increase underscores its superior noise-handling. Wav2Vec2’s 20.7% surge suggests a training bias toward clean audio.
4.4 Overall Model Rankings
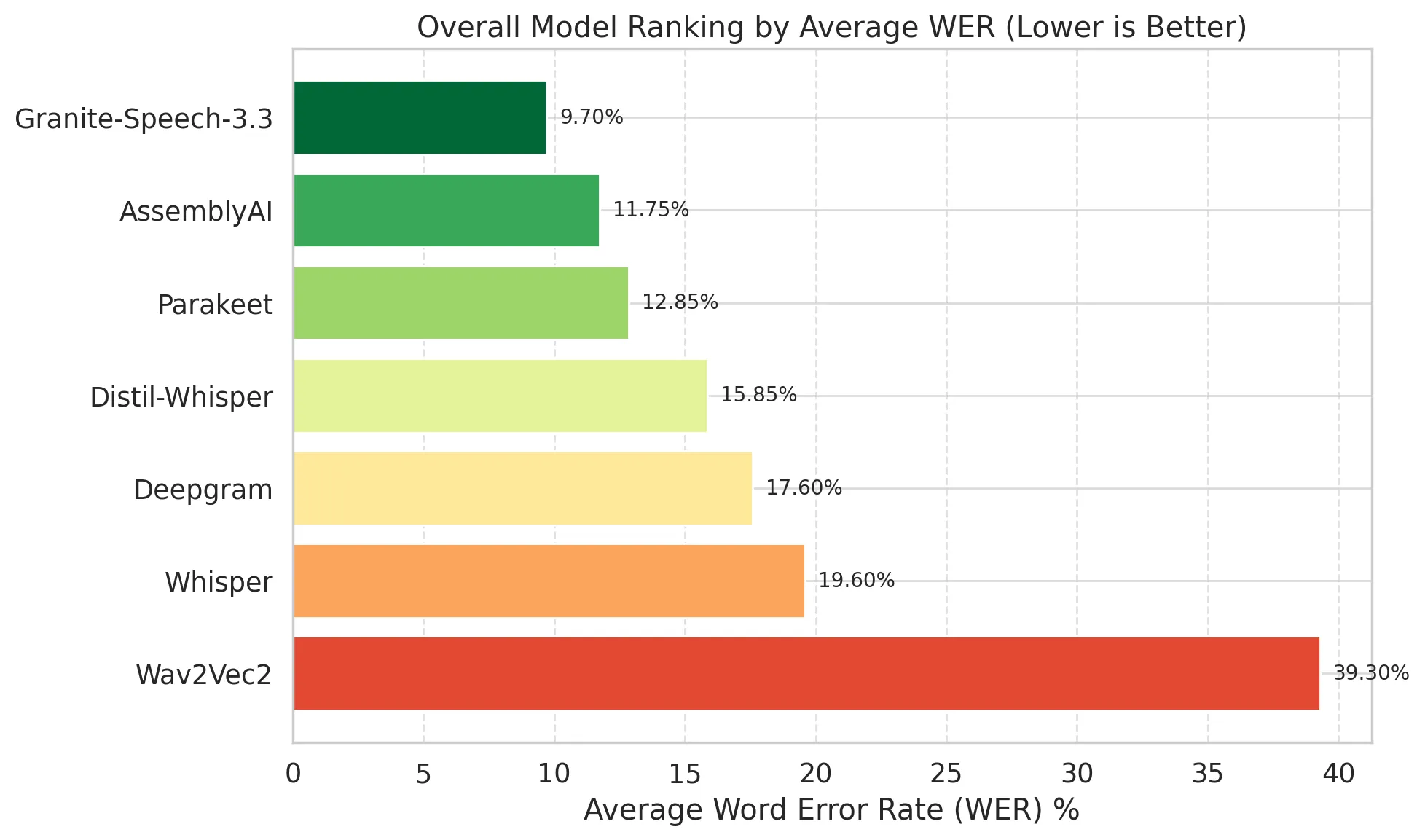
| Rank | Model | Average WER |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Granite-Speech-3.3 | 9.7% |
| 2 | AssemblyAI | 11.75% |
| 3 | Parakeet | 12.85% |
| 4 | Distil-Whisper | 15.85% |
| 5 | Deepgram | 17.6% |
| 6 | Whisper | 19.6% |
| 7 | Wav2Vec2 | 39.3% |
5 Limitations of This Benchmark
- Small Dataset Size: The benchmark uses only 58 audio clips, which limits the statistical significance of the results.
- English-Only Evaluation: All evaluations were done on English audio, excluding insights into multilingual performance.
- No Conversational or Overlapping Speech: The dataset consists of clear, single-speaker recordings.
- Limited Accent Representation: The sample size per accent group was too small for reliable fairness analysis.
- No Domain-Specific Vocabulary: The benchmark does not include technical terms from areas like healthcare or law.
- No Speed or Latency Testing: The focus was on transcription accuracy, not compute efficiency.
- No Prompt or Context Optimization: All models were tested in zero-shot mode without prompt engineering or conversational context.
6 Key Insights and Use Case Recommendations
- Granite-Speech-3.3:
- Best for: Mission-critical tasks (medical transcription, legal documentation, financial services, live accessibility) due to its precision and adaptability.
- AssemblyAI:
- Best for: Live captioning, voice commands. Its noise resilience suits real-time uses.
- Parakeet:
- Best for: Medical transcription and accessibility applications where missing words are unacceptable.
- Distil-Whisper:
- Best for: Educational content transcription, podcast/media subtitling, and live captioning where cost or speed may prioritize over perfection.
- Deepgram:
- Best for: Educational content, podcasts.
- Whisper:
- Best for: Interview documentation, meeting notes, and non-critical meetings.
- Wav2Vec2:
- Not recommended for production use due to unreliability, especially in noisy environments.
7 Conclusion and Future Work
This benchmark provides a comprehensive and unbiased evaluation of leading speech-to-text models under realistic conditions. Our findings clearly indicate that IBM Granite-Speech-3.3 stands out as the top performer, demonstrating exceptional accuracy and robustness across both clean and noisy audio environments. Distil-Whisper emerges as a strong contender among open-source models, offering a compelling balance of accuracy and efficiency. Conversely, Wav2Vec2 consistently underperformed, suggesting it is not yet ready for production-grade deployment in scenarios demanding high accuracy.
While this benchmark provides valuable guidance, it also highlights areas for future research. Expanding the dataset to include a wider variety of accents, conversational speech with overlapping speakers, and domain-specific vocabulary would further enhance the realism and applicability of such evaluations. Additionally, incorporating metrics for inference speed, latency, and computational efficiency would provide a more complete picture for real-time and edge computing applications. For organizations seeking to implement STT solutions, understanding these nuanced performance characteristics is paramount.